Optical prism is a multi-surface body made of transparent optical materials, and each surface is flat. Optical prisms can be used to disperse or fold light beams. Therefore, optical prism types can be roughly divided into two categories, one is a dispersion prism and the other is a reflection prism. Dispersion prisms are usually used in spectroscopic instruments to split composite light into beams of multiple wavelengths.
Compared with dispersion prisms, reflection prisms are more widely used. Reflection prisms can be seen in cameras, telescopes, microscopes and various medical instruments.
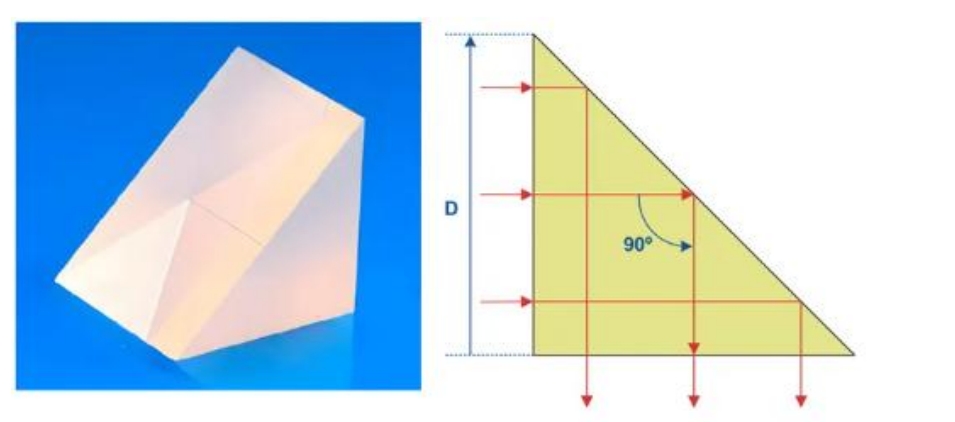
The cross section of a right-angle prism is a right triangle. The optical surface includes two right-angle surfaces and one inclined surface. Usually, a light beam is incident from one right-angle surface. After being reflected by the inclined surface, the light beam will be bent 90 degrees and emerge from another right-angle surface, as shown in the figure below:
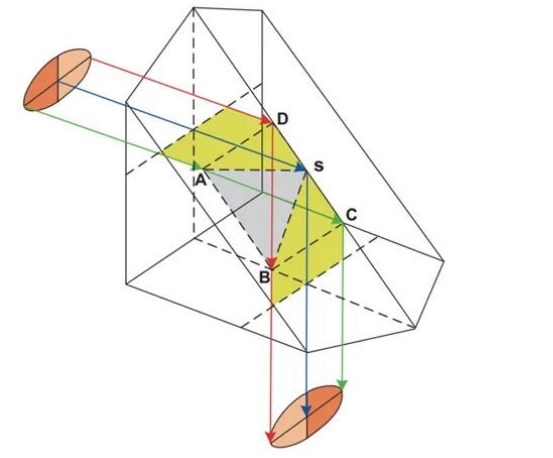
Based on the right angle prism, the inclined surface of the right angle prism is divided into two surfaces, and raised upward to form the shape of a roof. The two surfaces are perpendicular to each other, and it becomes a roof right angle prism. The light path diagram of the roof right angle prism is shown below. The light beam entering the prism will first be folded at the ridge, swapping the left and right parts of the image, and then emitting.